After many rounds of testing, we believe the five methods below are the simplest and most effective to unblock websites at school:
- Use a VPN or VPN extension: The most effective way to unblock websites at school.
- Use a Web Proxy: The fastest way to bypass school web restrictions.
- Use Mobile Data: A free way to access websites blocked on school WiFi.
- Use a URL Shortener: A simple, free tool for beating URL-based website blocks.
- Use the Wayback Machine: The best way to access restricted content without breaking any school policy.
Use the table below to compare these five unblocking methods side by side:
| Method |
Efficacy |
Speed |
Free or Paid? |
Works on Personal Device? |
Works on School Computer? |
Works on School Chromebook? |
Similar Alternatives |
| VPN Extension |
High |
Very Fast |
Free or Paid |
Yes |
No |
Unlikely |
Proxy Browser Extension |
| Web Proxy |
Medium |
Fast |
Free |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
URL Unblocker |
| Mobile Hotspot |
Very High |
Very Fast |
Free |
Yes |
Unlikely |
Yes |
Change Network Proxy |
| URL Shortener |
Low |
Very Fast |
Free |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
IP Search, Mobile Site |
| Wayback Machine |
Medium |
Fast |
Free |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Google Cache |
We’ll now take a closer look at each of these methods and how to use them to unblock websites at school.
1. Use a VPN Extension
| Pros |
Cons |
| The most effective way to access blocked websites at school |
Schools sometimes block access to VPN extensions from browsers’ web stores |
| Delivers very quick connection speeds |
The very best VPN extensions require a paid subscription |
| Provides a very high degree of encryption to protect your internet privacy and security |
|
| Good selection of free server locations to choose from |
|
The most reliable, safe, and effective way to unblock websites at school is to set up and use a VPN application. It’s by far the best method for bypassing website blocks.
A VPN works by creating a tunnel for your internet traffic to travel through. To do this, it re-routes your connection via a remote VPN server (the school’s local network will only see this server’s IP address).
Most school website blocks are based on the URL or IP address of the website you’re visiting. A VPN hides these details inside the VPN tunnel, bypassing content restrictions at school.
The problem is it’s almost always impossible to use VPN software since administrators configure school devices to prevent unauthorized software being installed on them.
The next best thing is therefore to use a VPN browser extension, instead. Below are simple instructions on how to install one on your web browser.
How to Use a VPN Extension
We’ve already explained how to use a VPN extension earlier in this guide, however as a quick recap:
- Find a trusted free VPN extension to your web browser via its Web Store. We suggest either CyberGhost or Windscribe.
- Add the VPN plugin to your web browser.
- Open the web extension and turn it on. Connect to a nearby server location for the fastest possible speeds.
- Visit the blocked website. The website should now be unblocked.
2. Use a Web Proxy
| Pros |
Cons |
| Free and very easy to use |
Rarely works with multimedia content and streaming sites, such as YouTube |
| Accessible via any browser, including Chrome, Safari and Firefox |
School administrators sometimes block the web proxy itself |
| Requires no manual installation or set up |
Only works within a single browser tab |
| Works well on school Chromebooks and school computers |
Doesn’t encrypt your connection, leaving your activity visible to teachers and network administrators |
|
Unsafe web proxies can spy on your activity or infect your session with malware |
If you can’t add a VPN extension to your web browser, then a good alternative to unblock websites at school is to use a web proxy. They’re free to use, fairly reliable at bypassing school restrictions, and don’t require any setup.
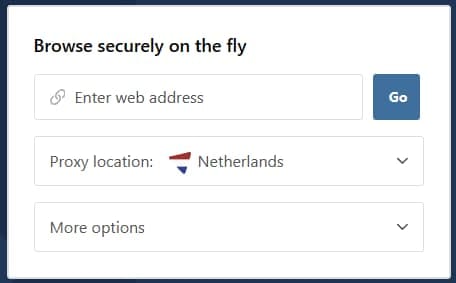
Hide.me’s web proxy service.
A web proxy is essentially a website with access to a proxy server embedded inside. You simply enter the blocked website’s URL, and the web proxy retrieves the site’s content for you in the same browser window.
This lets you bypass school blocks because you don’t actually request the website’s URL or IP address — the web proxy requests it on your behalf. This means the school’s content filters are not triggered.
WARNING: If your school uses more advanced filtering techniques, your web proxy connection could still be blocked. Similarly, if your device has screen monitoring built-in (which is common on school Chromebooks) your administrator can always see what you’re doing, even if you’re using a web proxy.
Web proxies tend to deliver reasonably fast connection speeds, and they’re a great option for unblocking text-based websites, such as Reddit. Gaming websites sometimes work, but streaming platforms are almost always blocked.
Further down we list a number of safe web proxies you can try.
Importantly, web proxies aren’t encrypted, unlike VPNs. This makes it easier for the school and its ISP to monitor you. Never enter any personal or sensitive information while using a web proxy.
Web proxies aren’t infallible, though, since schools can prevent access to them by adding the proxy’s URL to the network’s blocklist. If that’s the case, we suggest trying a URL Unblocker tool.
Similarly to a web proxy, URL Unblockers use another computer to access the blocked website on your behalf, bypassing school restrictions in the process. To do this, they typically use an embedded version of the Chromium browser which you can control from within the tool.
URL Unblockers are often less private, more insecure, and slower than a web proxy. But, they are less commonly blocked by school administrators and often work with video streaming websites. You can find examples of URL Unblockers on Replit.
How to Use a Web Proxy
To unblock websites at school with a web proxy:
- Go to a web proxy in your browser. We recommend Hide.me’s free proxy.
- Input the blocked website’s URL. On some web proxies, you can also pick a server location.
- Click ‘Visit Anonymously’. It will retrieve the site’s content for you without being blocked.
3. Switch to Mobile Data
| Pros |
Cons |
| Lets you access any website (that isn’t blocked by your cell phone provider) |
Requires a cell phone with good signal and a large data plan |
| Usually offers quick speeds |
Won’t work with certain website blocks on a school Chromebook |
| Works for streaming, gaming, and other multimedia websites |
You may get in trouble if caught on your phone during class |
| Prevents the school network administrator from monitoring your activity |
Won’t let you bypass device-level content filters, cell phone provider content and domain blocks |
Accessing the internet through your phone’s data network, rather than the school’s WiFi network, is an easy and quick way to unblock websites at school.
Most school content filters are implemented at the network-level. When you use the school’s WiFi, your traffic passes through a firewall in the local network which monitors the URL, IP address, and sometimes even the content of the website you’re visiting.
It compares this against a blocklist, and if it detects a match, your connection is blocked.
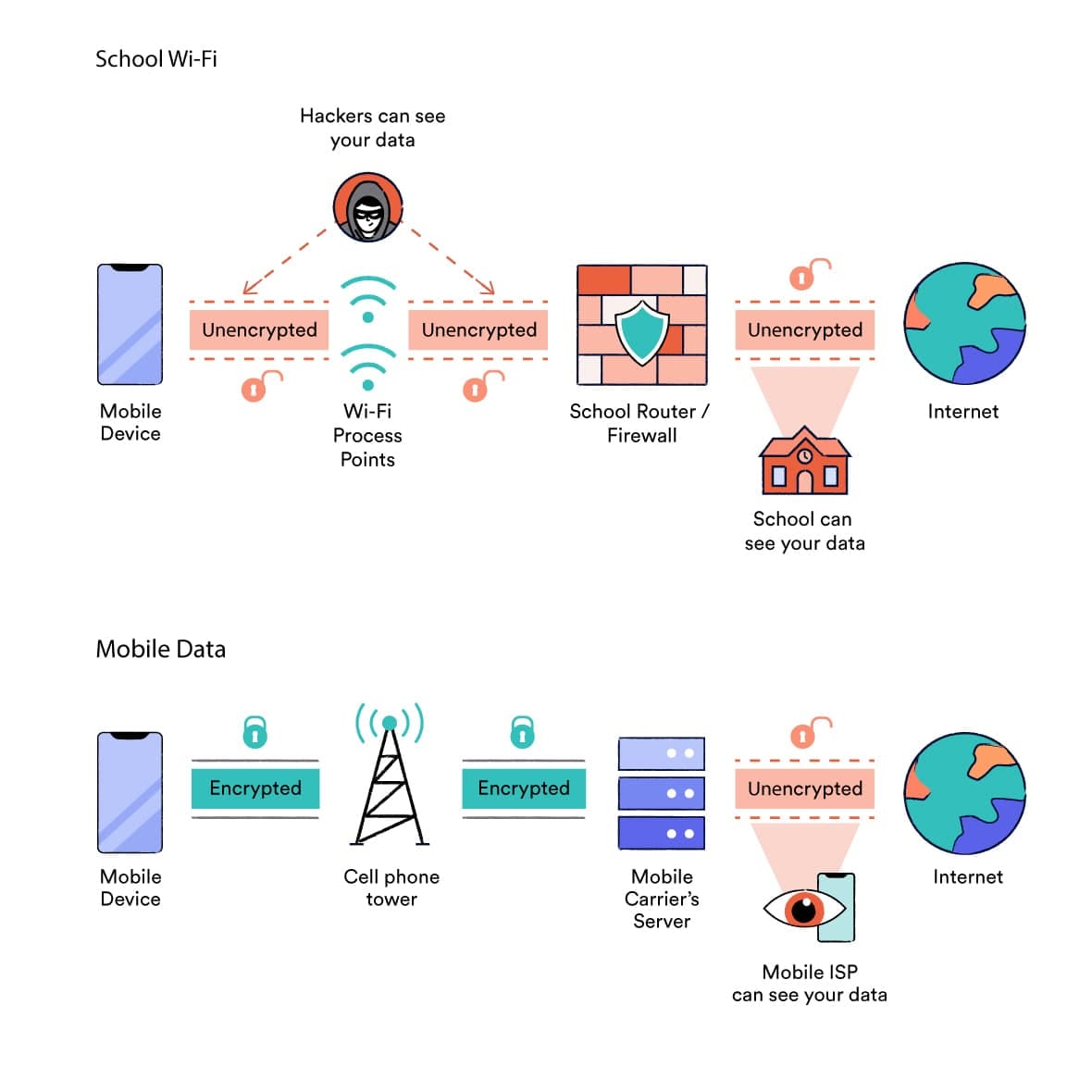
The difference between school WiFi and mobile data internet connections.
You can bypass these firewalls completely by switching from the school’s WiFi to your mobile data network.
When you use mobile data to access the internet, you’re no longer subject to school restrictions. You can access whichever websites your cell phone provider allows – often with faster speeds.
By turning your phone into a personal hotspot, you can use this method to unblock websites on school chromebooks and sometimes school computers too. That’s because your computer’s traffic is routed through your cell phone provider’s network and not your school’s network.
EXPERT TIP: Personal hotspots are visible to any device nearby. That means your teacher can often see when someone in the class has created a personal hotspot. You can change the hotspot’s name so it doesn’t give your identity away, but you can’t completely hide it.
It’s worth remembering that this method will consume your phone’s data allowance, which can quickly become expensive. You may also get in trouble if you’re caught using your phone in class.
In addition to these limitations, this method won’t work in two particular situations:
- Some schools configure student Chromebooks to always route your traffic through the school’s servers, regardless of which local network the Chromebook is connected to.In this case, your school’s content filters always apply, regardless of which network you’re connected to.
NOTE: Many schools switch their content filters off during out-of-school hours. This gives you unrestricted internet access at home, but it doesn’t stop your activity being routed through the school’s servers. It also doesn’t help to unblock websites during school hours.
- School computers and school chromebooks occasionally have content filtering software installed directly onto the device itself, in addition to network-level firewalls. That means website blocks will still apply regardless of whether you’re connected to a mobile data network or the school’s WiFi.
How to Use Mobile Data to Unblock Websites at School
To switch to cellular data on a smartphone device:
- Tap Settings.
- Open WiFi.
- Toggle the button to WiFi Off.
- A 3G, 4G or 5G symbol should appear at the top of your screen to signal that you’re now connected to mobile data.
To unblock websites on a school Chromebook, on a school computer, or on a personal laptop at school, you’ll need to turn your smartphone into a Personal Hotspot.
Here’s how to do this, using a school Chromebook as our example:
- On your cell phone, go to Settings.
- On Android devices, tap Network & Internet and then Hotspot and Tethering. On iPhone devices, tap Mobile Data and then Personal Hotspot.
- Turn On the Personal Hotspot. Set the password and change the hotspot name to something anonymous.
- On your Chromebook, open WiFi Settings via the tab in the bottom-right corner of the screen.
- Find your smartphone’s Personal Hotspot among the available WiFi networks.
- Connect to it by entering the password on your phone.
- Navigate to the blocked website, which should be unblocked now.
4. Use a URL Shortener
| Pros |
Cons |
| Free to use |
Only unblocks URL-based content filters |
| No manual installation or configuration needed |
Administrators sometimes block students from accessing URL shorteners |
| Can unblock streaming, gaming, and social media websites |
|
| Works on school Chromebooks and school computers |
|
A URL shortener is a free online tool that takes a full URL address and creates a shortened version that is easier to remember and share. When accessed, the shortened URL then redirects users to the original, longer URL.
URL shorteners are mostly used to create more user-friendly URLs, but they can also be used to unblock websites at school. That’s because the tool lets you visit blocked websites via a URL that isn’t recognised by the school’s content filters.
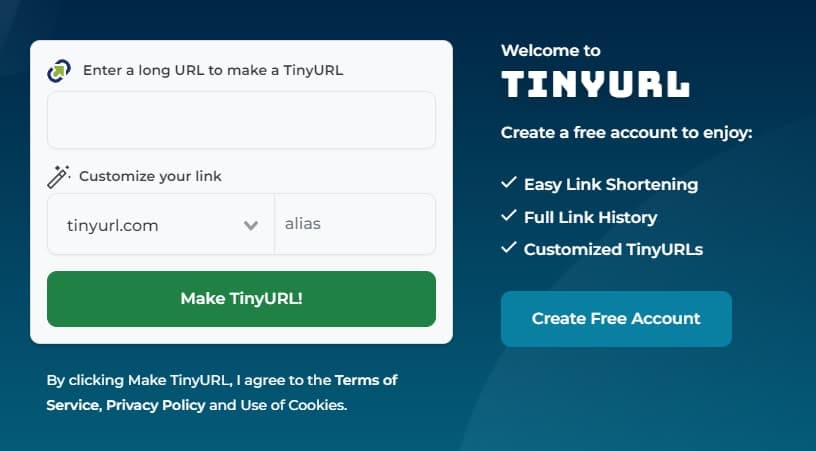
TinyURL can be used to bypass internet restrictions at school.
It’s therefore a great method for easily bypassing URL-based website blocks, which are the most common type of school restriction. It can be used for streaming and gaming, and works equally well on personal devices, school computers, and school chromebooks.
WARNING: If your school filters content based on IP addresses or something more sophisticated, this method will not work.
Sometimes, school administrators block access to the URL shortener website itself. In this case, you’ll need to find one that isn’t blocked. Popular URL shorteners include TinyURL, Ow.ly and Bitly.
It’s important to keep in mind that your network administrator can still see what you’re doing when you use a URL shortener at school.
How to Use a URL Shortener
To unblock websites at school using a URL shortener:
- Go to a URL Shortener website in your browser. We recommend TinyURL or Bitly.
- Input the URL of the blocked website you want to access. Press “Enter”.
- Copy the shortened URL that is generated.
- Paste that URL into your browser.You should be redirected to the website without being blocked.
5. Use Wayback Machine
| Pros |
Cons |
| Unlikely to get you into trouble |
The content may be outdated |
| Free and simple to use |
Doesn’t work well for sites that are regularly updated or rely on real-time data processing. |
| Requires no software installation or configuration |
Some schools block the Wayback Machine website |
| Works well on school Chromebooks and school computers, e.g. in the library |
|
Another technique for unblocking websites at school is to access a copy of the website, rather than trying to visit the blocked site itself. The best way to do this is to use the Wayback Machine.
The Wayback Machine is a free digital archive containing billions of web page copies. The tool works by taking snapshots of websites and then storing them in its database.
By viewing an archived version of the site, you prevent the school’s content filters from detecting the URL or IP address of the blocked website, thereby granting you free access to the restricted material.
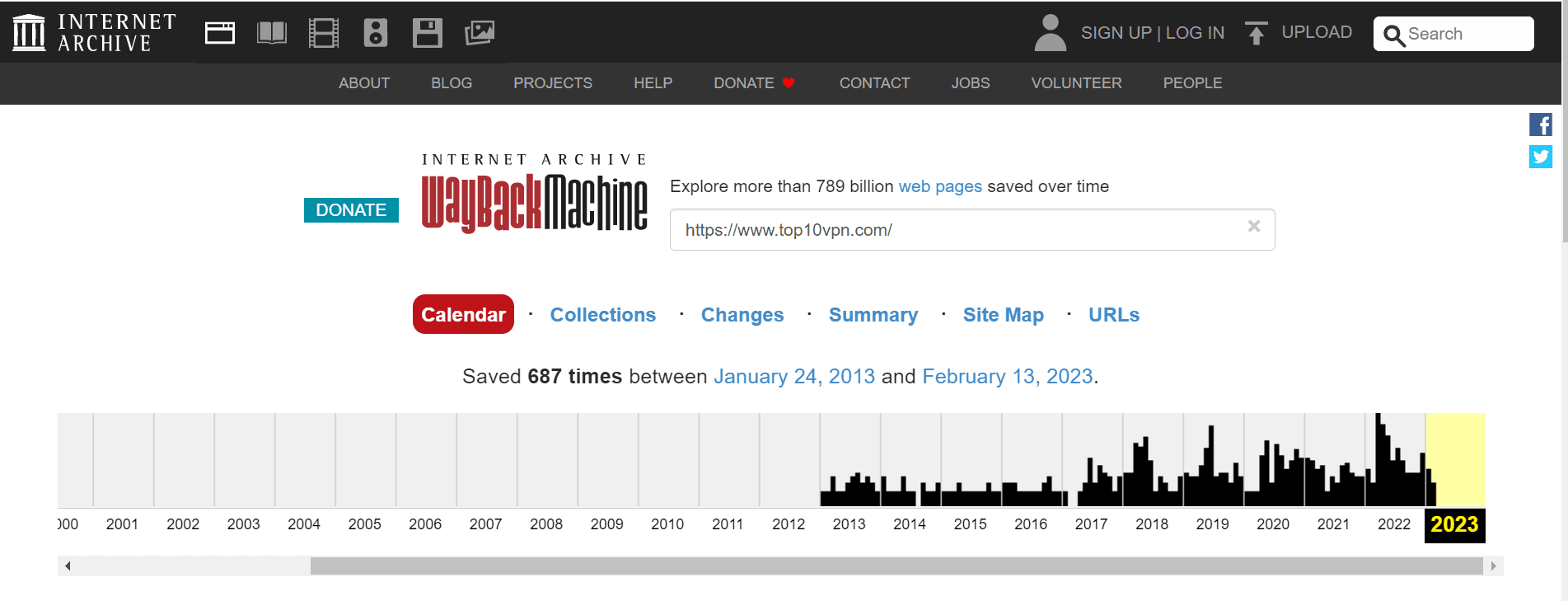
The Wayback Machine is a digital archive of the internet.
Using the Wayback Machine is a quick and easy way to bypass simple website blocks at school, and it requires no manual installation or configuration.
It works on school Chromebooks and school computers (unless the URL has been added to the school network’s blacklist), and is probably the method that’s least likely to cause any issues with your teacher or administrator.
That said, it does have its limitations. The archived version of the website may not always be the most up to date. Additionally, some websites may not be fully functional or interactive when accessed through the Wayback Machine.
For this reason, this method is best for unblocking text-based websites. The tool supports multimedia content (such as video or audio streaming) for some but not every website. It won’t work for games, either.
How to Use the Wayback Machine
We used the Wayback Machine to unblock Instagram at school.












